General
S3 is Object-based storage and not suitable for operating system, which need block base storage.
Data is spread across multiple devices and multiple facilities.
Files can be from 0 Bytes to 5 TB.
S3 is a universal namespace. Names must be unique globally.
Sample of S3 web address : https://gateway53.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/ or https://gateway53.s3.amazonaws.com/ (if created in North Virginia which is the default region)
When you upload a file to S3, you will receive a HTTP 200 code if the upload was successful.
Object consist of:
- Key : name of the object
- Value : data of object, made up of sequence of bytes
- Version Id : for versioning purposes
- Metadata : data about data that you are storing
- Subresources : Access Control Lists (permissions), Torrent
You can restrict access to individual objects or buckets using Access Control Lists
You can protect deletion of objects, by using MFA (Multi Factor Authentication)
S3 Bucket URL Styles
Virtual Hosted Style URL
Virtual style puts your bucket name 1st, s3 2nd, and the region 3rd.
https://awsexamplebucket1.eu.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/homepage.html
Path Style Access URL
Path style puts s3 1st and your bucket as a sub domain.
https://s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/awsexamplebucket1.net/homepage.html
Static web site URL
S3 static hosting can be your own URL or your bucket name 1st, s3-website 2nd, followed by the region.
Legacy Global Endpoint URL
Legacy Global endpoint has no region.
https://www.my-registered-domain/index.html
AWS are in the process of phasing out Path style, and support for Legacy Global Endpoint format is limited and discouraged.
Multipart Upload
Multipart upload delivers improved throughput.
Multipart upload delivers the ability to pause and resume object uploads.
Multipart upload delivers the ability to begin an upload before you know the final object size
Multipart upload delivers quick recovery from network issues.
Data Consistency Model
Read after Write Consistency for PUTS of new Objects
Eventual Consistency for overwrite PUTS and DELETES (can take some time to propogate)
S3 has the following guarantees from Amazon:
- Built for 99.99% availability for the S3 platform.
- Amazon guarantee 99.99% availability.
- Amazon guarantees 99.999999999% durability for S3 information
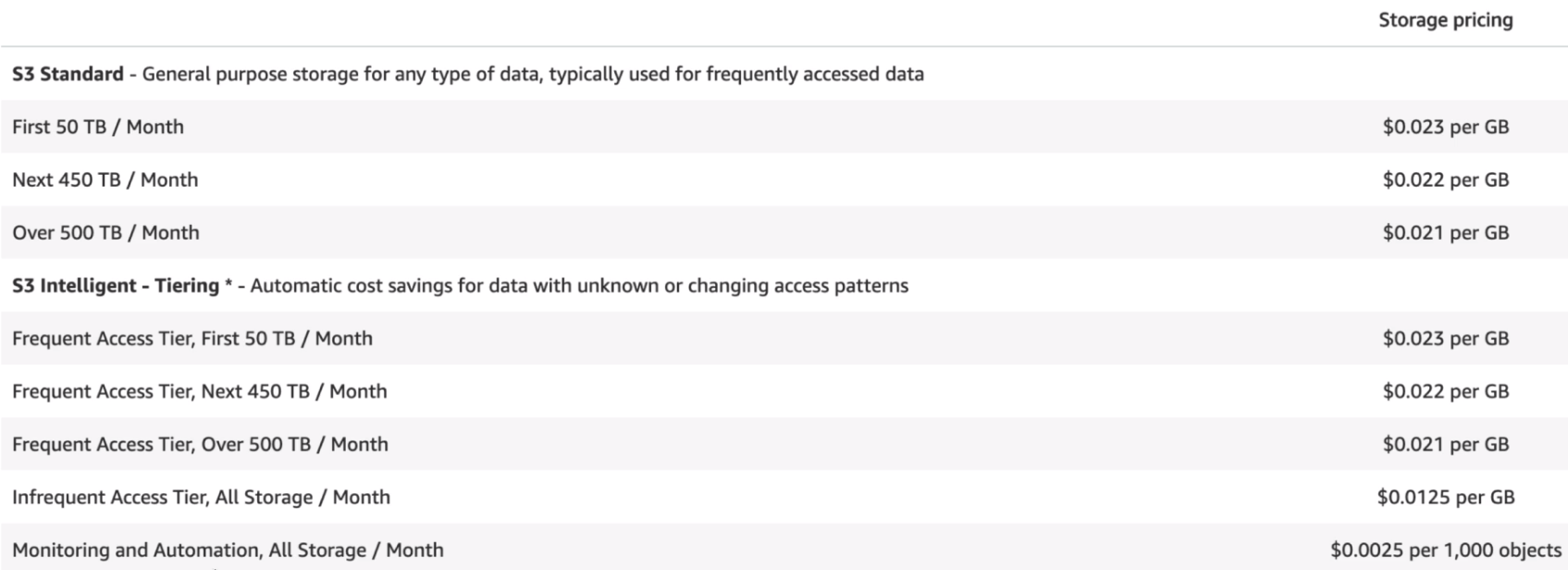
S3 Storage Classes
S3 Standard
99.99% availability
99.999999999% durability
Stored redundantly across mutiple devices in multiple facilities, and is designed to sustain the loss of 2 facilities concurrently.
S3 - IA (Infrequently Accessed), previously RRS (Reduced Redundancy Storage)
For data that is accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access when needed.
Lower fee than S3, but you are charged a retrieval fee
Standard - IA is designed for larger objects and has a minimum object size of 128KB. Objects smaller in size will incur storage charges as if the object were 128KB.
S3 - One Zone - IA
For where you want a lower-cost option for Infrequently accessed data, but do not require the multiple AZ data resilience.
S3 - One Zone - IA is the recommended storage for when you want cheaper storage for infrequently accessed objects.
It has the same durability but less availability. There can be cost implications if you use it frequently or use it for short lived storage.
S3 - Intelligent Tiering
Designed to optimize costs by automtically moving data to the most cost-effective access tier, without performance impact or operational overhead.
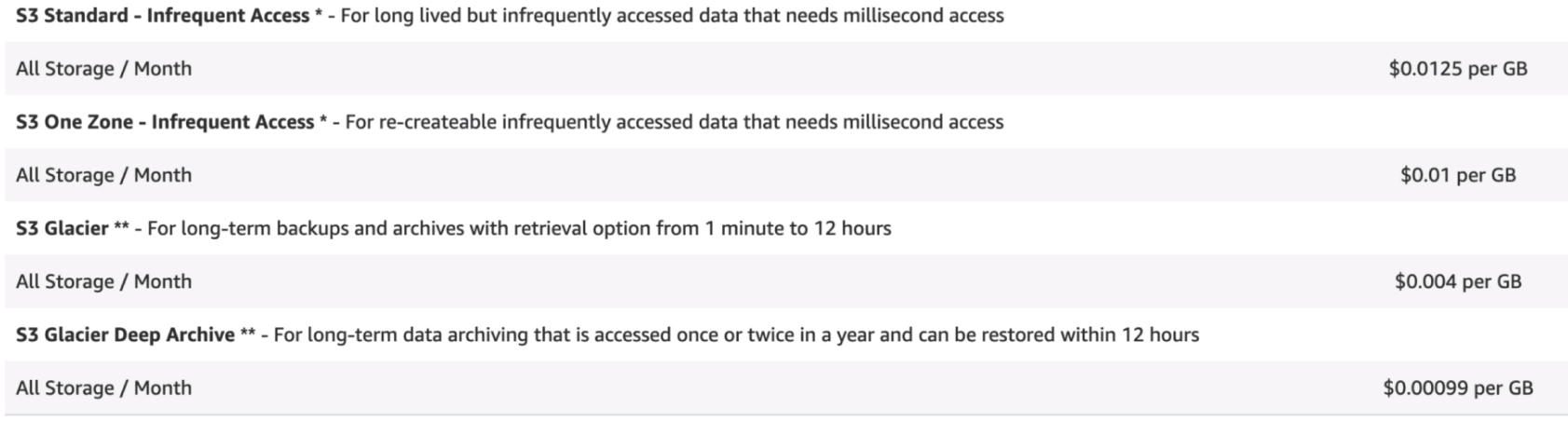
S3 - Glacier
Secure, durable, and low-cost storage class for data archiving
You can reliably store any amount of data at costs that are competitive with or cheaper than on-premises solutions.
Retrieval times configurable from minutes to hours.
Because Amazon S3 maintains the mapping between your user-defined object name and Amazon Glacier’s system-defined identifier, Amazon S3 objects that are stored using the Amazon Glacier option are only accessible through the Amazon S3 APIs or the Amazon S3 Management Console.
S3 - Glacier Deep Archive
Lowest cost storage class where retrieval time of 12 hours is acceptable.
S3 - Comparison
| S3 Standard | S3 Intelligent Tiering | S3 Standard IA | S3 One Zone IA | S3 Glacier | S3 Glacier Deep Archive | |
| Durability | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | 99.999999999% (11 9's) | 99.999999999% (11 9's) |
| Availability | 99.99% | 99.9% | 99.9% | 99.5% | N/A | N/A |
| Availability SLA | 99.9% | 99% | 99% | 99% | N/A | N/A |
| Availability Zones | >= 3 | >= 3 | >= 3 | 1 | >= 3 | >= 3 |
| Min capacity charge per object | N/A | N/A | 128KB | 128KB | 40KB | 40KB |
| Min storage duration charge | N/A | 30 days | 30 days | 30 days | 90 days | 180 days |
| Retrieval fee | N/A | N/A | per GB retrieved | per GB retrieved | per GB retrieved | per GB retrieved |
| First byte latency | milliseconds | milliseconds | milliseconds | milliseconds | minutes or hours | hours |
S3 - Charging
Storage
Requests
Storage Management Pricing
Data Transfer Pricing
Transfer Acceleration
S3 Transfer Acceleration utilises the CloudFront Edge Network to accelerate your uploads to S3. Instead of uploading directly to your S3 bucket, you can use a distinct URL to upload directly to an edge location which will then transfer that file to S3. You will get a distinct URL to upload to: gateway53.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com. You can use the Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration Speed Comparison tool to compare accelerated and non-accelerated upload speeds across Amazon S3 regions. The Speed Comparison tool uses multipart uploads to transfer a file from your browser to various Amazon S3 regions with and without using Transfer Acceleration.
Cross Region Replication Pricing
Features
Cross Region Replication
For High Availability and Disaster Recovery you might want to replicate your buckets to different regions around the world.
When Cross Region Replication is enabled every object that gets added to your bucket automtically gets replicated to the replicate bucket.
S3 Transfer Acceleration
Enables fast, easy and secure transfers of files over long distances between your end users and an S3 bucket.
Transfer Acceleration takes advantage of Amazon CloudFront's globally distributed edge locations.
As the data arrives at an edge location, data is routed to Amazon S3 over an optimized network path (Amazon backbone network)
Tiered Storage
Lifecycle Management
Automate moving your objects between the different storage tiers.By adding a prefix/tag value, you specify that only objects with this prefix or tag will be subject to this rule.
You can select lifecycle configuration for current and previous versions and set up transitions from the different storage classes.
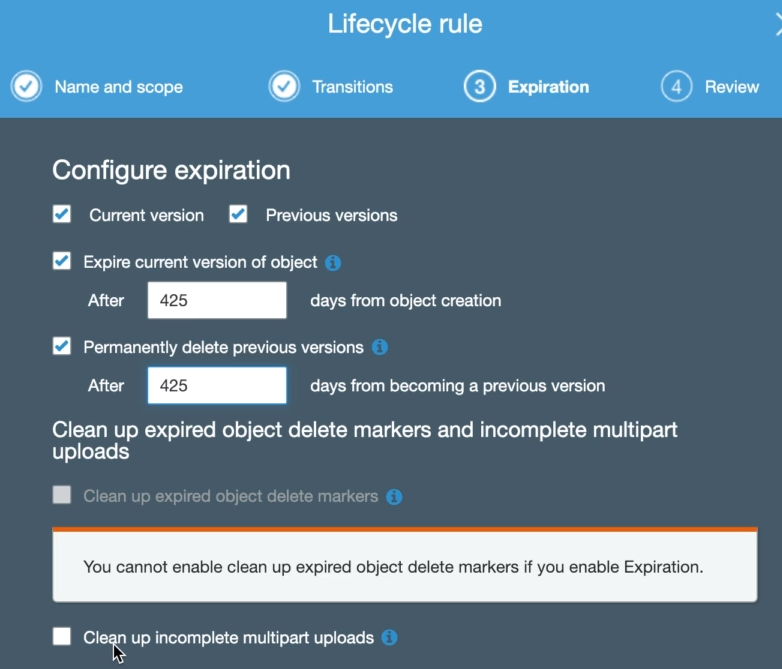
You can also configure when objects should expire and clean up incomplete multipart uploads.
Version Control
Stores all versions of an object (including all writes and even if you delete an object). Once enabled, versioning cannot be disabled, only suspended. You have to create a new bucket to completely turn off versioning. Integrates with Lifecycle rules. Versioning MFA Delete capability can be used to provide an additional layer of security. Uploading a new file using versioning will change the permissions of the file. If version 1 of the file was public and you upload a new version, the new version will not be public anymore.To show versions of an object you can click the Show button next to Versions. The size of your S3 bucket will go up exponentially if you have versioning enabled and you make changes to large file. Each new version of a file is stored as a complete new object! When hiding versioning by clicking on the Hide button and than selecting the fiel and delete, a delete marker will be placed on the file and it will not show anymore. However when you click on the Show button again, you can delete the delete marker to restore the file to its latest version.
If versioning is displayed by clicking the Show button, you can select specific versions to delete.
Security & Encryption
By default, all newly created buckets are PRIVATE. You can setup access control to your buckets using: - Bucket Policies - Access Control Lists S3 buckets can be configured to create access logs which log all requests made to S3 bucket. This can be sent to another bucket and even another bucket in another account. Encryption in Transsit (accessing https site) is achieved by: - SSL/TLS Encryption at Rest (server side, encryption on stored data) is achieved by: - S3 Managed Keys - SSE-S3 - (Server Side Encryption) AWS manage the keys for you - AWS Key Management Service, Managed Keys - SSE-KMS - You and AWS are managing the keys together - Server Side Encryption with Customer Provided Keys - SSE-C - You give Amazon keys that you manage - Client Side Encryption Using an encryption client library, such as the Amazon S3 Encryption Client, you retain control of the keys and complete the encryption and decryption of objects client-side using an encryption library of your choice. Some customers prefer full end-to-end control of the encryption and decryption of objects; that way, only encrypted objects are transmitted over the Internet to Amazon S3.
MFA Delete
Access Control Lists & Bucket Policies
S3 - Creating Bucket
Making an object public
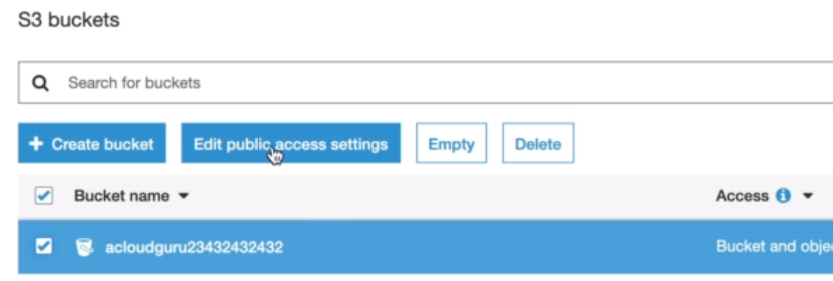
Select your bucket and then click on the Edit public access settings.
Uncheck the 'Block all public access' option and click Save.
You can now click on your object and then on Actions and Make public.
https://aws.amazon.com/s3/faqs/
Sharing S3 Buckets across Accounts
Different ways to share S3 buckets across accounts
- Using Bucket Policies & IAM (applies across the entire bucket). Programmatic Access Only, so won't be able to use the console. - Using Bucket ACL & IAM (individual onjects). Programmatic Access Only. - Cross-account IAM Roles. Programmatic and Console accwss
Cross-account IAM Roles
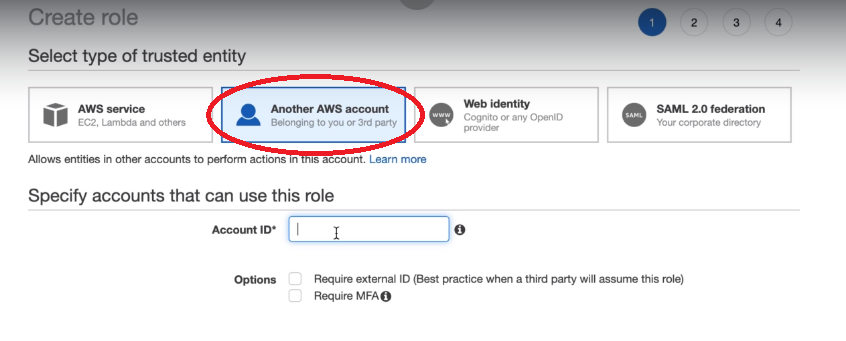
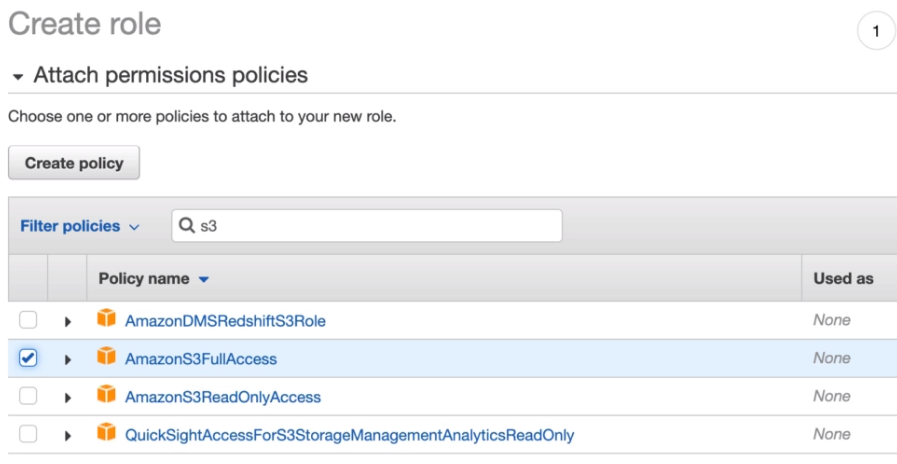
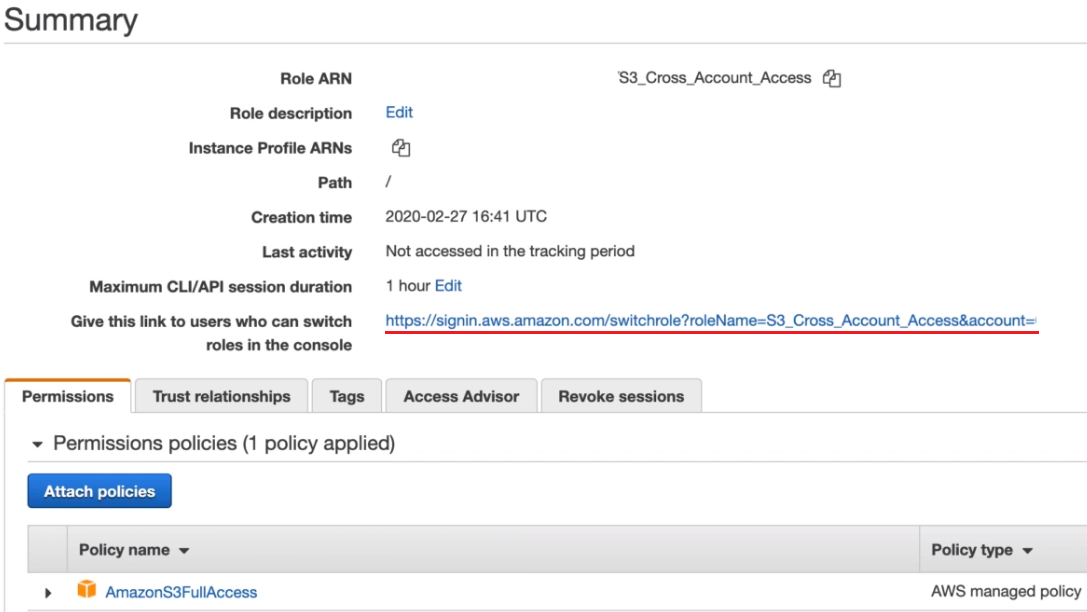
Copy this link, sign out and sign into your other AWS Account and add a new user in IAM with Console Access
Create a group with Administrator Rights and add user to this group.
Sign In as newly created user
If you click on your user dropdown, you will see a new option called 'Switch Role'
To setup the 'Switch Role', paste the link into your browser.
All neccessary values will be automatically completed, click the Switch Role button
You will now be logged in to the cross account, but will only have access to the S3, as this is the only permissions given to this account
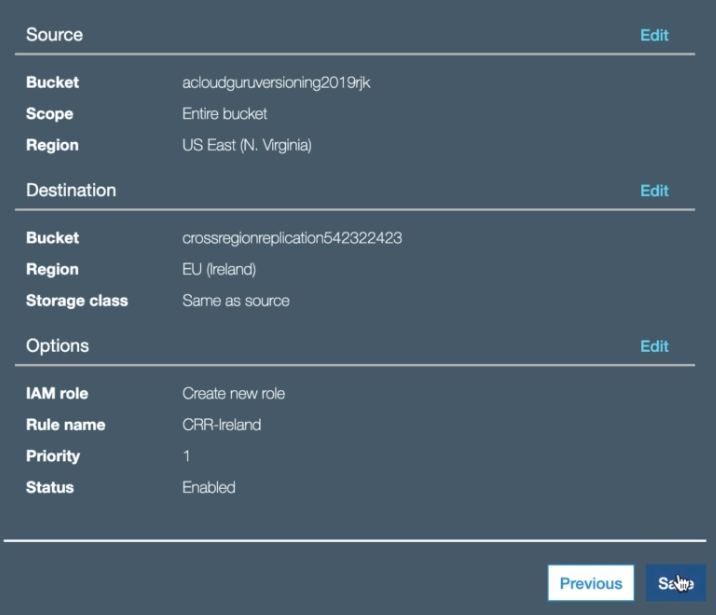
S3 - Cross Region Replication
- Click on your S3 bucket and selct Management and then Replication. - Click 'Add rule'. - You will be prompted that the bucket does not have versioning enabled, which is a requirement for Cross Region Replication. - Versioning must be enabled on both the source and destination buckets for replicaton to work. - So enable versioning for your bucket and then setup a new rule as seen below:
- When setting up Cross Region Replication, the existing objects in the source bucket will not be replicated automatically. - You will have to upload existing objects manaully. - New objects or subsequents updated objects in the original bucket will be replicated to the replication bucket. - Deleting individual versions or delete markers will not be replicated.
S3 Content Privacy
CloudFront signed URLs and signed cookies provide the same basic functionality: they allow you to control who can access your content.
If you want to serve private content through CloudFront and you're trying to decide whether to use signed URLs or signed cookies, consider the following:
Use signed URLs for the following cases:
- You want to use an RTMP distribution. Signed cookies aren't supported for RTMP distributions.
- You want to restrict access to individual files, for example, an installation download for your application.
- Your users are using a client (for example, a custom HTTP client) that doesn't support cookies.
Use signed cookies for the following cases:
- You want to provide access to multiple restricted files, for example, all of the files for a video in HLS format or all of the files in the subscribers' area of a website.
- You don't want to change your current URLs.
S3 Extra
Until 2018 there was a hard limit on S3 puts of 100 PUTs per second. To achieve this care needed to be taken with the structure of the name Key to ensure parallel processing. As of July 2018 the limit was raised to 3500 and the need for the Key design was basically eliminated. You can use the Multipart Upload API to upload very large files to S3. AWS S3 has four different URLs styles that it can use to access content in S3. Virtual Hosted Style URL
Puts your bucket name 1st, s3 2nd, and the region 3rd Path-Style Access URL (phasing out) Puts s3 1st and your bucket as a sub domain Static Website URL
S3 static hosting can be your own domain or your bucket name 1st, s3-website 2nd, followed by the region Legacy Global Endpoint URL (limited and discouraged)
Has no region. How many S3 buckets can I have per account dy default? 100