DNS
Description
Very first route in America that went from one side of the country to the other was Route 66.
DNS is actually on port 53, so this is where the name Route53 came from.
DNS is used to convert human friendly domain names (https://www.gateway53.com) into an IP address (https://48.434.43.4)
IP addresses are used by computers to identify each other on the network and comes into 2 forms (IPv4 and IPv6).
.com is a top level domain name.
.co.uk : .uk is the top level domain name and .co is the second level domain name.
Top level domains are controlled by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
You can view this database at http://www.iana.org/domains/root/db.
SOA (Start Of Authority) record
Every DNS address start with a SOA record.
The SOA record stores information about:
- The name of the server that suppllied the data for the zone
- The administrator of the zone
- The current version of the data file
- The default number of seconds for time-to-live file on resource records
NS (Name Server Records)
They are used by Top Level Domain servers to direct traffic to the Content DNS server which contains the automatic DNS records.

Difference between Alias Record and a CNAME
CNAME does not work with naked domains, Alias record does
Alias Records
Alias Records have special functions that are not present in other DNS servers.
Their main function is to provide special functionality and integration into AWS services.
Unlike CNAME records, they can also be used at the Zone Apex, where CNAME records cannot.
Alias Records can also point to AWS Resources that are hosted in other accounts by manually entering the ARN
MX Records
Used for mail
PTR Records
Reverse of A-Record, looking up a name against a IP Address
Route 53 has a security feature that prevents internal DNS from being read by external sources. The work around is to create a EC2 hosted DNS instance that does zone transfers from the internal DNS, and allows itself to be queried by external servers
ELB (Elastic Load Balancers)
Description
ELB's do not have pre-defines IPv4 addresses; you resolve to them using a DNS name.
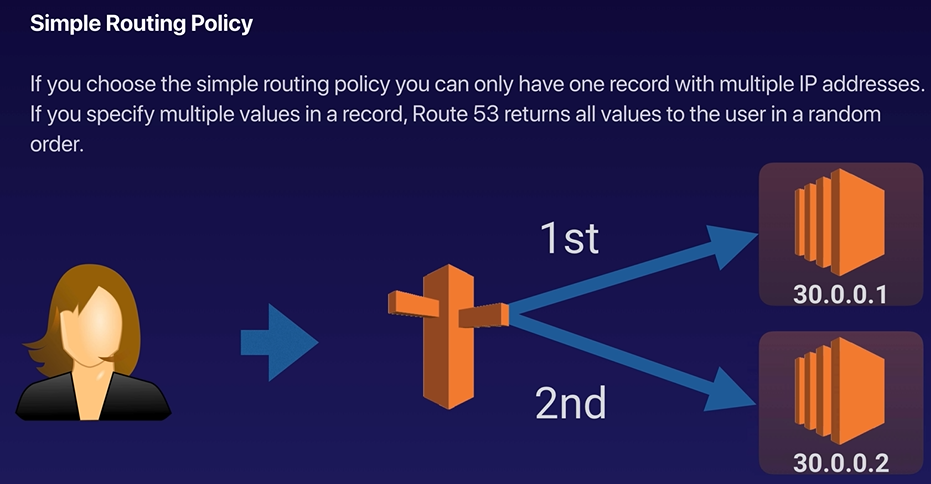
Route53
The following Routing Policies are available with Route53:
- Simple Routing
- Weighted Routing
- Latency-based Routing
- Failover Routing
- Geolocation Routing
- Geoproximity Routing
- Multivalue Answer Routing