Theory
Relational databases on AWS - RDS (OLTP)
SQL Server
Oracle
MySQL Server
PostgreSQL
Aurora
MariaDB
Oracle
Oracle RAC (Real Application Clusters) is a shared-everything database cluster technology from Oracle that allows a single database (a set of data files) to be concurrently accessed and served by one or many database server instances.
Deploying Oracle RAC on Amazon EC2 allows you leveraging the elasticity and scalability of Amazon Web Services.
You can deploy scalable Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) on Amazon EC2.
Backups
There are 2 different types of Backups for RDS: Automated Backups and Database Snapshots Whenever you restore either an Automatic Backup or a manual Snapshot, the restored version of the database will be a new RDS instance with a new DNS endpoint. Encryption at rest is supported for MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MarioDB & Aurora. Encryption is done using the AWS Key Management Service (KMS) service. Once your RDS instance is encrypted, the data stored at rest in the underlying storage is encrypted, as are its automated backups, read replicas, and snapshots.Automated Backups
- Allow you to recover your database to any point in time within a retention period. - The retention period can be between 1 and 35 days. - Will take a full daily snapshot and will also store transaction logs throughout the day. - When you do a recovery, AWS will first choose the most recent daily backup, and then apply transaction logs relevant to that day. - This allows you to do a point in time recovery down to a second, within the retention period. - Enabled by default. The backup data is stored in S3 and you get free storage space equal to the size of your database. - So if you have an RDS instance of 10Gb, you will get 10Gb worth of storage. - Backups are taken within the defines window. - During the backup window, storage I/O may be suspended while your data is being backed up and may experience elevated latency.Database Snapshots
- Done manually. They are stored even after you delete the original RDS instance, unlike automated backups.
Key Features
Multi-AZ : For Disaster Recovery with Automatic Failover
- EC2 instances pointing to our Primary Database with a DNS address hosted by AWS and use to point to your database. - If you lost your Primary Database, Amazon will detect that and automatically update your DNS address to point to your secondary database. - So failover is automatic with Multi-AZ. - Muti-AZ allows you to have an exact copy of your production database in another AZ. - AWS handles the replication for you, so when your production database is written to, this write will automatically be synchromized to the stand by database. - In the event of planned database maintenance, DB instance failure, or an AZ failure, Amazon RDS will automatically failover to the standby so that database operations can resume quickly without administrative intervention. - Multi-AZ is available for the following databases: - SQL Server - Oracle - MySQL Server - PostgreSQL - MariaDB - When you update a database to enbale Multi-AZ, you can force a failover, but Rebooting your DB Instance and selecting the 'Reboot With Failover' option. - When you create or modify your DB instance to run as a Multi-AZ deployment, Amazon RDS automatically provisions and maintains a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. - Updates to your DB Instance are synchronously replicated across Availability Zones to the standby in order to keep both in sync and protect your latest database updates against DB instance failure.
Read Replicas : For Performance
- EC2 instances pointing to our Primary Database with a DNS address hosted by AWS and use to point to your database. - Everytime you do a write to your Primary Database, the write will be replicated to another database (Read Replica) in a different AZ. - If you lose your Primary Database, there is no automatic failover. - You will have to create a new DNS Url and then update your EC2 instances to use the new Url pointing to your Read Replica database. - The advantage with Read-Replicas is that you can point half of your EC2 instances to read from your Primary Database and half to read from your Read-Replica. - You can have up to 5 copies of Read-Replicas. - Read Replicas allow you ro have a read-only copy of your production database. - This is achieved by using Asynchronous replication from the primarily RDS instance to the read replica. - You use read replicas primarily for very read-heavy database workloads. - Read Replicas are available for the following databases: - MySQL Server - PostgreSQL - MariaDB - Oracle - Aurora - Used for scaling, not for DR! - Must have automatic backups turned on in order to deploy a read replica. - You can have read replicas of read replicas. (but watch out for latency). - Each read replica will have its own DNS end point. - You can have read replicas that have Multi-AZ. - You can create read replicas of Multi-AZ source databases. - Read replicas can be promoted to be their own databases. This breaks the replication. - You can have a read replica in a second region. - You can also use Read-Replicas to migrate your MySQL database to Aurora. - To turn Read-Replica on you select your database > Actions > Create Read Replica - You can promote your Read-Replica to a primary database by selecting your Read-Replica > Actions > Promote read replica
Authentication
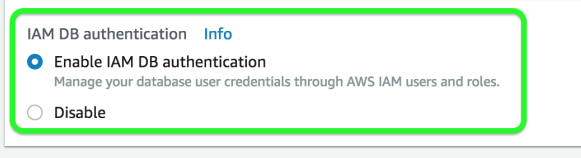
You can authenticate to your DB instance using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) database authentication. IAM database authentication works with MySQL and PostgreSQL. With this authentication method, you don't need to use a password when you connect to a DB instance. Instead, you use an authentication token. An authentication token is a unique string of characters that Amazon RDS generates on request. Authentication tokens are generated using AWS Signature Version 4. Each token has a lifetime of 15 minutes. You don't need to store user credentials in the database, because authentication is managed externally using IAM. You can also still use standard database authentication.
Non-Relational databases on AWS
Collection = Table
Document = Row
Key Value Pairs = Fields
What is Data Warehousing?
Used for business intelligence.
Tools like Cognos, Jaspersoft, SQL Server Reporting Services, Oracle Hyperion, SAP NetWeaver.
Used to pull in very large and complex data sets.
Usually used by management do do queries on data (performance vs targets).
OLTP vs OLAP
- OLTP stands for Online Transaction Processing - OLAO stands for Online Analytics Processing - These 2 differ from each other in terms of the types of queries you will run: - OLTP Example - Order number 2120121, pulls up a row of data such as Name, Date, Address, Delivery Status ect. - OLAP Example - Net Profict for EMEA and Pacific for the Digital Radio Product. Pulls in large numbers of records: - Sum of Radios sold in EMEA. - Sum of Radios sold in Pacific. - Unit cost of Radio in each region. - Sales price of each Radio.
Amazon's Data Warehouse solution is called Redshift. (OLAP)
Exam Questions
- RDS Reserved instances are available for multi-AZ deployments. (TRUE/FALSE) TRUE - MySQL installations default to port number: 3306 - What data transfer charge is incurred when replicating data from your primary RDS instance to your secondary RDS instance? There is no charge - If you are using Amazon RDS Provisioned IOPS storage with a Microsoft SQL Server database engine, what is the maximum size RDS volume you can have by default? 16TB - In RDS, changes to the backup window take effect when? Immediately - When you add a rule to an RDS DB security group, you must specify a port number or protocol. (TRUE/FALSE) FALSE
Technically a destination port number is needed, however with a DB security group the RDS instance port number is automatically applied to the RDS DB Security Group.