Load Balancer Types
| Application Load Balancer |
Best suited for load balancing of HTTP and HTTPS traffic. They operate at Layer 7 and are application-aware. They are intelligent, and you can create advanced request routing, sending specified requests to specific web servers. The ALB has functionality to distinguish traffic for different targets (mysite.co/accounts vs. mysite.co/sales vs. mysite.co/support) and distribute traffic based on rules for target group, condition, and priority. |
| Network Load Balancer |
Best suited for load balancing of TCP traffic where extreme performance is required. They operate at connection level Layer 4 and are able to handle millions of requests per second, while maintaining ultra-low latencies. The Network Load Balancer is specifically designed for high performance traffic that is not conventional web traffic Can obtain a fix IP address. |
| Classic Load Balancer |
Legacy load balancers. You can load balance HTTP/HTTPS applications and use Layer 7 specific features such as (X-Forwarded and sticky sessions) You can also use strict Layer 4 load balancing for applications that rely purely on the TCP protocol. If your application stops responding, the ELB (Classic Load Balancer) responds with a 504 error. This means that the application is having issues and could be either at the Web Server layer or the Database Layer. |
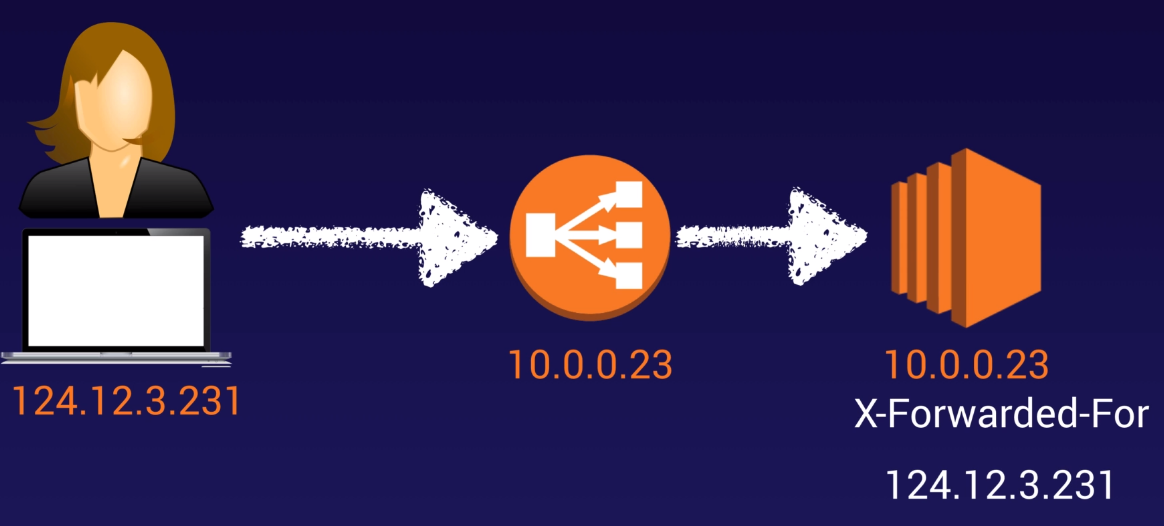
When a user request goes through you classic load balancer, you EC2 instance receive the internal IP of the load balancer and not neccessary the IP from your user request.
You can use the X-Forwarded-For header value to still get the IP of your user request.
Create a Classic Load Balancer
Define Load Balancer
| Create LB inside | Choose VPC to create the load balancer in |
| Create an internal load balancer | Load balancer that is inside a private subnet. |
| Enable advanced VPC configuration |
This will allow you to choose the Subnets that you load balancer will be deploy into. Should always have a minimum of 2 Subnets in different AZs. |
| Listener Configuration | Add listener setup like HTTP/HTTPS ect |
Assign Security Groups
Create a new security group or select an existing security group.Configure Security Settings
Configure Health Check
| Ping Protocol | Protocal to use when checking ping status |
| Ping Port | Port to use when checking ping status |
| Ping Path | Page to use when checking ping status |
| Response Timeout | Time to wait when receiving a response from the health check (2 to 60s) |
| Interval | The amount of time between health checks (5 to 300s) |
| Unhealthy threshold | Number of consecutive health check failures |
| Healthy threshold | Number of consecutive health check successes |
Add EC2 instances
Select your EC2 instances| Enable Cross-Zone Load Balancing | Cross-Zone Load Balancing distribute traffic evenly across all targets in the AZs enabled for the load balancer. |
| Enable Connection Draining | The number of seconds to allow existing traffic to continue flowing. |
Add Tags
Review
Check if all details are correct and click 'Create'Next steps
You never get an IP for your load balancer, you get a DNS record/name.
Now you can browse to the DNS address of your load balancer.
Check if Instances are in 'InService', by selecting you load balancer and clicking on the Instances tab.
If it says that Instances are 'OutOfService', you just have to wait for your Health Checks to pass.
You can now browse to you DNS address, and you will see that the load balancer will interchange between you EC2 instances.
If you stop one of your EC2 instances, the Health Check will fail and it will be removed from the Instances in the Load Balancer.
Application Load Balancer
Target Group
EC2 > LOAD BALANCING > Target Groups
Your load balancer routes requests to the targets in a target group using the target group settings that you specify, and performs health checks on the targets using the health check settings that you specify.
| Target type |
- Instance : EC2 instances - IP : Could be web services that is not in AWS - Lambda function : Call a lambda function |
| VPC | Select VPC that this load balancer will recide in |
Health check settings
| Path | Path and name of file to test health check on for example /index.html |
Advanced health check settings
| Port |
traffic port override |
| Path | Path and name of file to test health check on |
| Healthy threshold | Number of consecutive health check successes required before considering an unhealthy target healthy (2 to 10s) |
| Unhealthy threshold | Number of consecutive health check failures required before considering an healthy target unhealthy (2 to 10s) |
| Timeout | The amount of time, in seconds, during which no response means a failed health check (2 to 120s) |
| Interval | The approximate amount of time between health checks of an individual target (5 to 300s) |
| Success codes | HTTP response code for successful test for example 200 |
Targets
Add Targets by selecting your Target Group and clicking on the Targets tab.
Click on Edit and select Instances to add to registered instances in Target Group
Create a Application Load Balancer
Configure Load Balancer
| Scheme | internet-facing () internal () |
| IP address type | ipv4 () dualstack () |
| VPC |
Select VPC and then public subnet (availability zones) You need at least 2 public subnets to create a Load Balancer |
Configure Security Settings
Configure Security Groups
Configure Routing
Register Targets
Review
Advanced Load Balancer Theory
Sticky Sessions
Classic Load Balancer routes each request independently to the registered EC2 instance wiht the smallest load.
Sticky sessions allow you to bind a user's session to the specific EC2 instance.
This ensures that all requests from the user during the session are sent to the same instance.
You can enable Sticky Sessions for Application Load Balancers as well, but the traffic will be sent at the Target Group Level.
If all your traffic is going to only 1 EC2 instance in a group of 2, the reason could be Sticky Sessions. You could resolve this issue by disabling Sticky Sessions.
Cross Zone Load Balancing
No Cross Zone Load Balancing
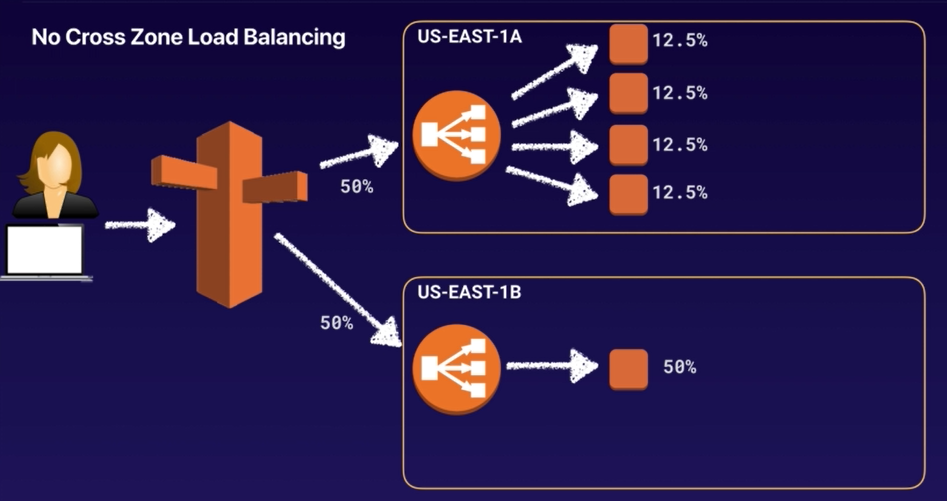
Route53 is splittng yout traffic 50/50 to 2 different AZs and in each of the AZs we have a classic load balancer.
In US-EAST-1A we have 4 EC2 instances and in US-EAST-1B we have only have 1 instance.
Because Cross Zone Load Balancing is not enabled, we cannot sent traffic from one AZ to another.
So the processing percentages will be uneven, as seen in the image above.
Cross Zone Load Balancing
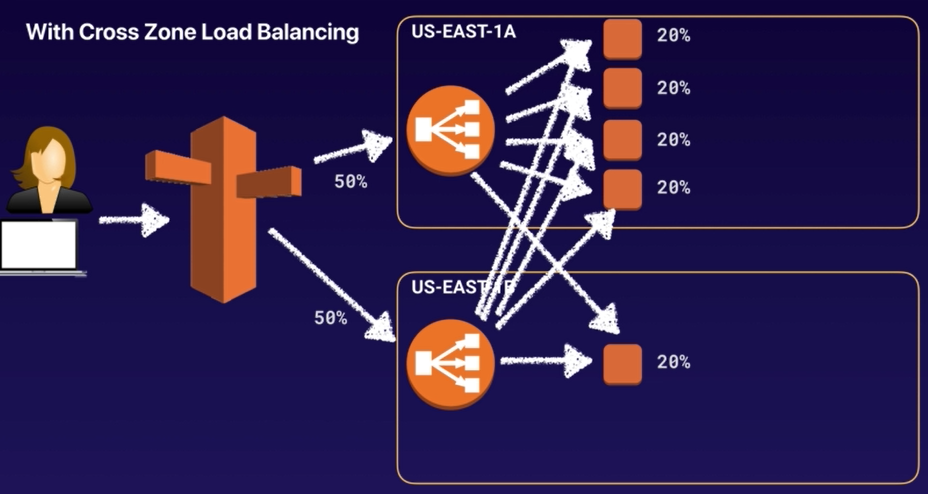
Route53 is splittng yout traffic 50/50 to 2 different AZs and in each of the AZs we have a classic load balancer.
In US-EAST-1A we have 4 EC2 instances and in US-EAST-1B we have only have 1 instance.
Because Cross Zone Load Balancing is enabled, traffic can be sent to different AZs.
Path Patterns
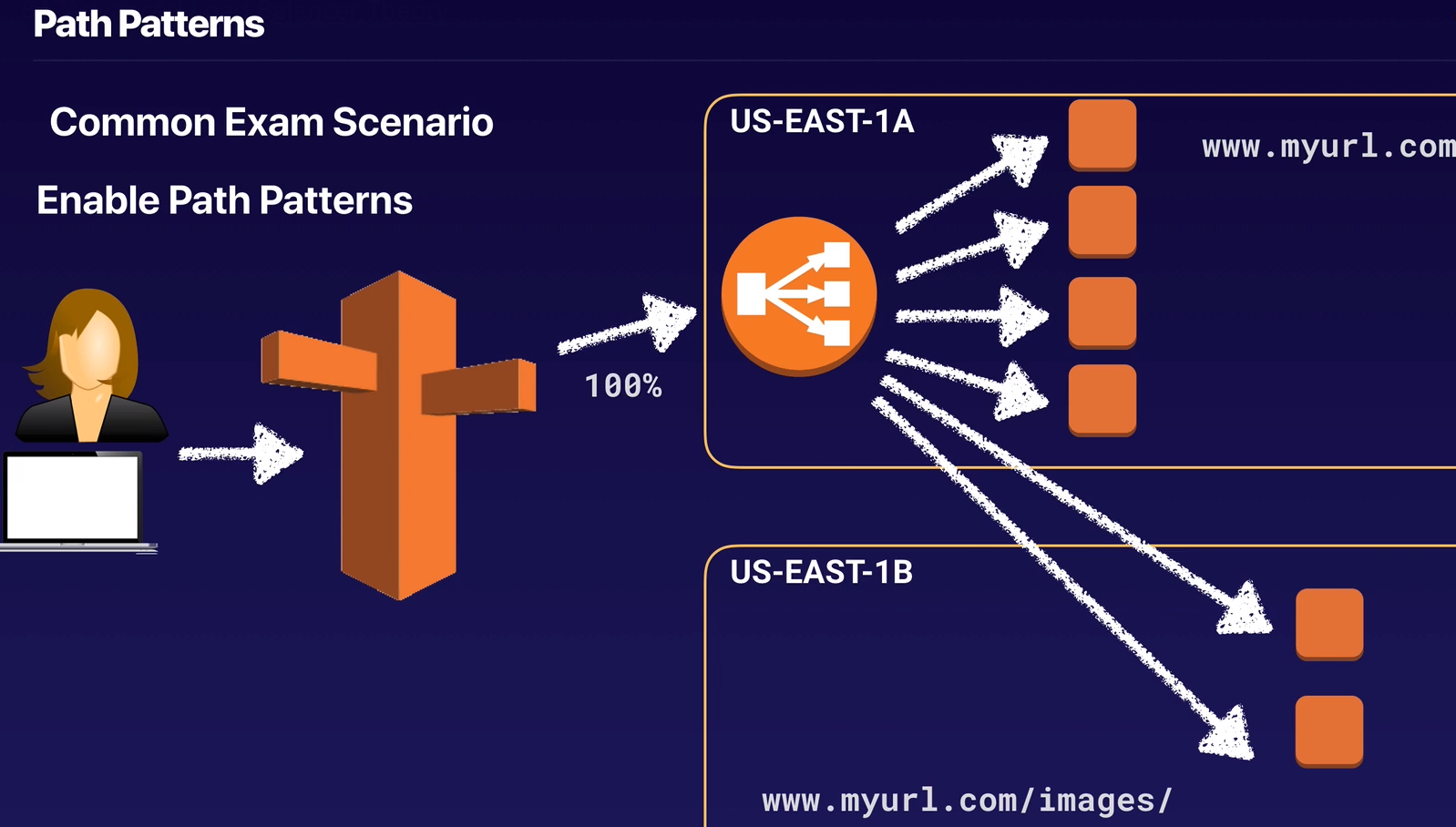
Path patterns allow you to direct traffic to different EC2 instances based on the URL contained in the request.
You can create a listener with rules to forward requests based on the URL path.
This is known as path-based routing.
If you are running microservices, you can route traffic to multiple back-end services using path-based routing.
For example, you can route general requests to one target group and requests to render images to another target group
Health Checks
Load balancers will route incoming requests only to healthy instances.
When the load balancer determines that an instance is unhealthy, it stops routing requests to that instance.
The load balancer resumes routing requests to the instance when it has been restored to a healthy state.
There are two ways of checking the status of your EC2 instances:
1. Via the Auto Scaling group
2. Via the ELB health checks
The default health checks for an Auto Scaling group are EC2 status checks only.
If an instance fails these status checks, the Auto Scaling group considers the instance unhealthy and replaces it.
If you attached one or more load balancers or target groups to your Auto Scaling group, the group does not, by default, consider an instance unhealthy and replace it if it fails the load balancer health checks.
However, you can optionally configure the Auto Scaling group to use Elastic Load Balancing health checks.
This ensures that the group can determine an instance's health based on additional tests provided by the load balancer.
The load balancer periodically sends pings, attempts connections, or sends requests to test the EC2 instances. These tests are called health checks.
If you configure the Auto Scaling group to use Elastic Load Balancing health checks, it considers the instance unhealthy if it fails either the EC2 status checks or the load balancer health checks.
If you attach multiple load balancers to an Auto Scaling group, all of them must report that the instance is healthy in order for it to consider the instance healthy.
If one load balancer reports an instance as unhealthy, the Auto Scaling group replaces the instance, even if other load balancers report it as healthy.
Questions
Yes, you can privately access Elastic Load Balancing APIs from your VPC by creating VPC endpoints.
With VPC endpoints, the routing between the VPC and Elastic Load Balancing APIs is handled by the AWS network without the need for an Internet gateway, NAT gateway, or VPN connection.
The latest generation of VPC Endpoints used by Elastic Load Balancing are powered by AWS PrivateLink, an AWS technology enabling the private connectivity between AWS services using Elastic Network Interfaces (ENI) with private IPs in your VPCs.
