What is EC2?
- Scaling out is where you have more of the same resource separately working in parallel (visualize services sitting side by side).
- Scaling up is where you make it bigger and bigger (CPU, Memory ect) after the initial design was finished.
- By default AWS has a limit of 20 instances per region
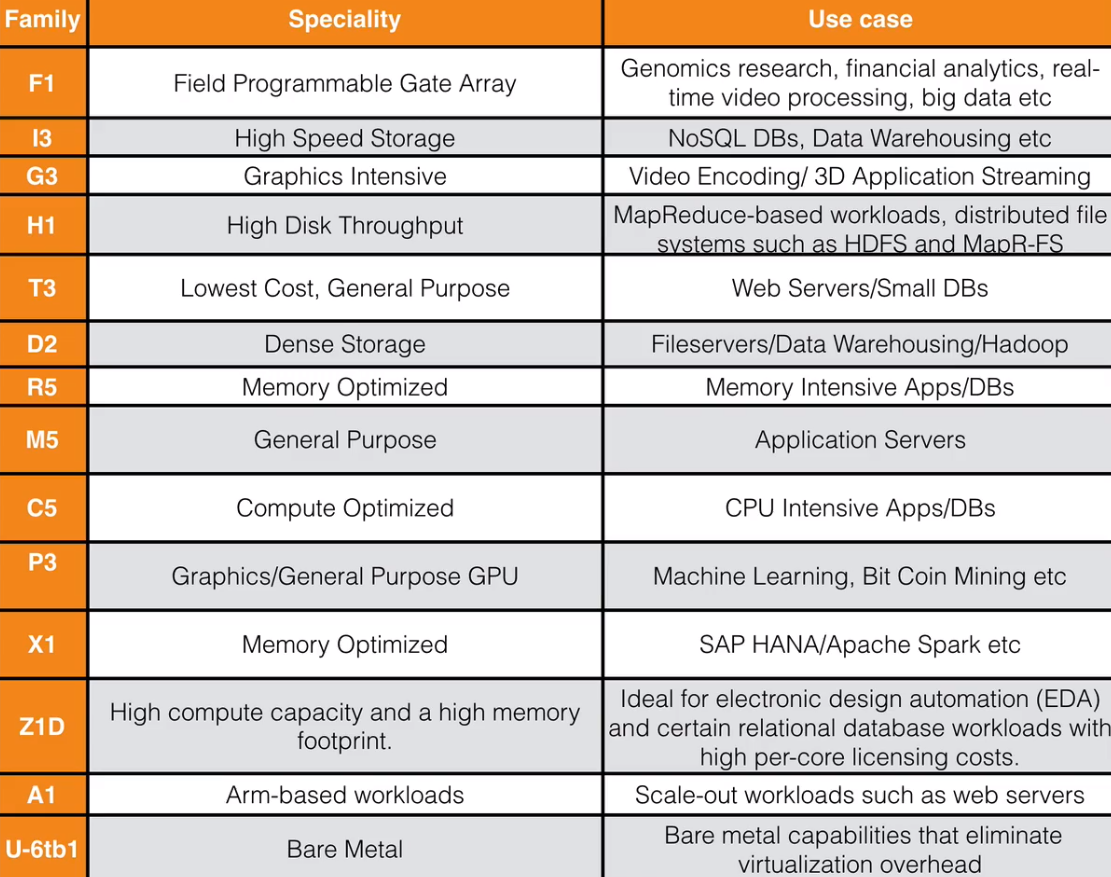
EC2 Types

EC2 Bash Scripting
Description
Create bootstrap scripts that will run when EC2 instance boots up.
At the 'Configure Instance' step, you can click on Advanced Details > User data.
This is where you can add your bash scripting.
| #!/bin/bash | Will always start with a this path to our interpreter |
| yum update -y | Do basic OS updates |
| yum install httpd -y | Install Apache service |
| service httpd start | Start Apache service |
| chkconfig httpd on | Make sure Apache service get started with a reboot |
| cd /var/www/html | Navigate to web page |
| echo "<html><h1>My Cloud Gateway EC2 instance</h1></html>" > index.html | Default text for website start page |
| aws s3 mb s3://gateway53s3bucket001 | Create S3 bucket |
| aws s3 cp index.html s3://gateway53s3bucket001 | Backup website to S3 bucket |
Instance Metadata
Description
You can SSH into your EC2 instance and view user and meta data.
ssh into your EC2 instance Display your bootstrap script (if any) of your EC2 instance:curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data/Give you different options of meta data for your EC2 instance:curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/Get your local IP address for this instance:curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4
EC2 Placement Groups
Description
The name you specify for a Placement Group must be unique within your AWS Account.
You can't merge placement groups.
You can move an existing instance into a placement group.
Before you move the instance, the instance must be in the stopped state.
You can move or remove an instance using the AWS CLI or AWS SDK, you CANT DO IT via the Console yet.
The 3 Placement Group types are:
-
Clustered Placement Group
Grouping of instances within a single AZ.
Clustered Placement groups are recommended for applications that need low network latency, high network throughput, or both.
Only certain instances can be launched into a Clustered Placement Group.
CAN'T span multiple Availability Zones.
AWS recommend homogenous (same instance type) instances when using Clustered Placement Groups. -
Spread Placement Group
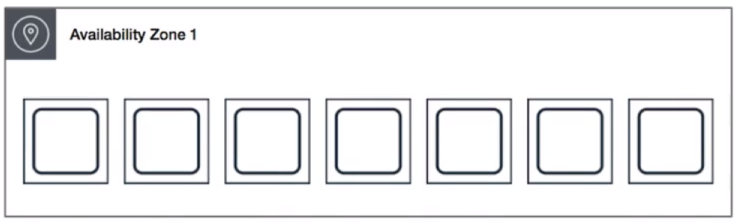
A spread placement group is a group of instances that are each placed on distinct underlying hardware.
Spread placement groups are recommended for applications that have a small nunber of critical instances that should be kept separate from each other.
You can have spread placement groups within different AZs within one region.
THINK INDIVIDUAL INSTANCES.
Spread placement groups have a specific limitation that you can only have a maximum of 7 running instances per Availability Zone. -
Partitioned Placement Group
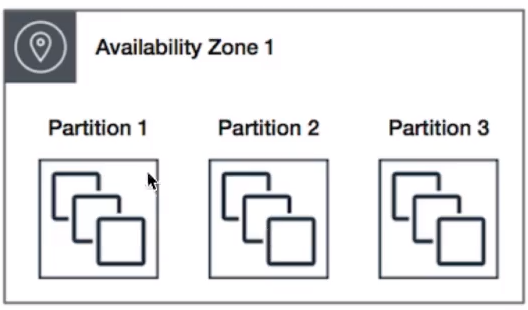
When using partition placement groups, Amazon EC2 devides each group into logical segments called partitions.
Amazon EC2 ensures that each partition within a placement group has its own set of racks.
Each rack has its own network and power source.
No two partitions within a placement group share the same racks, allowing you to isolate the impact of hardware failure within your application.
THINK MULTIPLE INSTANCES.
Multiple EC2 instances HDFS, HBase and Cassandra.
CAN span multiple Availability Zones.
EC2 Pricing Models
-
On Demand
Allows you to pay a fixed rate by the hour (or second) with no commitment.
Users that want the low cost and flexibility of Amazon EC2 without any up-front payment or long-term commitment.
Applications with short term, spiky, or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted.
Applications being developed or tested on Amazon EC2 for the first time. -
Reserved
Provides you with a capacity reservation, and offer a significant discount on the hourly charge for an instance.
Contract Terms are 1 Year or 3 Years Terms.
- Applications with a steady state or predictable usage. - Applications that require reserved capacity. - Users able to make upfront payments to reduce their total computing costs even further. - Depending on you type of RL you can modify the AZ, scope, network platform, or instance size (within the same instance type), but not Region.Reserved Pricing Tyoes
Standard Reserved Instances These offer up to 75% off on demand instances. The more you pay up front and the longer the contract, the greater the discount. You cannot convert instance types (for example a t2 micro to a t2 small) on Standard Reserved instancesConvertible Reserved Instances These offer up to 54% off on demand capability to change the attributes of the RI as long as the exchange results in the creation of Reserved Instances of equal or greater value. You can change between different instance types.Scheduled Reserved Instances These are available to launch within the time windows you reserve. This option allows you to match your capacity reservation to a predictable recurring schedule that only requires a fraction of a day, a week, or a month. -
Spot
Enables you to bid whatever price you want for instance capacity, providing for even greater savings. If the Spot instances is terminated by Amazon EC2, you will not be charged for a partial hour of usage. However, if you terminate the instance yourself, you will be charged for any hour in which the instance ran. Useful for: - Applications that have flexible start and end times. - Applications that are only feasible at very low compute prices. - Users with urgent computing needs for large amounts of additional capacity. -
Dedicated Hosts
Physical EC2 server dedicated for your use.
Dedicated Hosts can help you reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses.Dedicated Hosts pricing is useful for: - For regulatory requirements that may not support multi-tenant virtualization. - Great for licensing which does not support multi-tenancy or cloud deployments. - Can be purchased On-Demand (hourly) - Can be purchased as a Reservation for up to 70% off the On-Demand price.
Launch EC2 instance
Configure Instance Details
| Purchasing option | This is where you can request Spot Instances and set your Spot Price |
| Network |
Select your VPC to launch instance into The AZs is randomized. So eu-west-1a could be completely different than eu-west-1a in a different account. |
| Subnet | Select your Subnet (Availability Zone) |
| Auto-assign Public IP | This is enabled for public Subnets and disabled for private Subnets |
| Capacity Reservation | Reserve capacity for your instance in a specific Availability Zone |
| Shutdown behavior | Do you want to stop or terminate an instance when it is shutting down |
| Enable termination protection | Protection against accidently terminating an EC2 instance |
| Monitoring |
CloudWatch by default will monitor your instances every 5 minutes Selecting Enable ClouwWatch detailed monitoring will monitor your instance less that 5 min. |
| Advanced Details - User Data | This is where you can add bootstrap scripts to be applied to your EC2 instance at launch time. |
Add Storage
Root device volume can only launch on SSD or Magnetic Standard volume types.
EBS Root Volumes of your DEFAULT AMI's can be encrypted.
You can also use a third party tool (bit locker) to encrypt the root volume.
On an EBS-backed instance, the default action is for the root EBS volume to be deleted when the instance is terminated
Any additional EBS volumes will not be deleted by default. You have to set the 'Delete on Termination'option when creating these volumes or delete them manually.
Additional volumes can be encrypted.
Configure Security Group
- Security Groups is nothing other than a virtual firewall in the cloud.
Key Pair
Secure SSH Client for Windows Users (Chrome Extention)
- Google search for 'ssh chrome extension' and select the 'Secure Shell App - Google Chrome' searh result.
- Install extension on Chrome.
- To access this extension navigate to chrome://apps and select 'Secure Shell App'
- Configure Settings:
- username : ec2-user
- hostname : IP Address of EC2 instance
- To create Identity, you need to go your command prompt and navigate to the location of your Key-Pair (.pem) file.
- When you are in the same path as your Key-Pair file, type the following:
- ssh-keygen -y -f 'NameOfFile.pem' > 'NameOfFile.pub'
- That will create a public key file.
- Rename your private key file (basically loosing the extension):
- ren NameOfFile.pem NameOfFile
- Go back to the Secure Shell App and click on the Import button next to Identity and select your 2 Key-Pair files.
- Click Enter or Connect
Prep EC2 instance
- Look for OS updates:yum update -y- Install Apache (turning EC2 into a Web Server)yum install httpd -y- Navigate to:cd /var/www/html- Anyting you put in here will be available as a website. - To turn on the Apache service:service httpd start- chkconfig will restart your Apache (httpd) service if your EC2 instance reboots.chkconfig on
EC2 Details
Status Checks
- 'System Status Checks', checks the underlying hypervisor (physical machine) - 'Instance Status Checks', checks the EC2 instance itself
Auto Scaling
In an Auto-Scaling group the instance in the group with the most EC2 instances and the olderst launch configuration will terminate first when the group is scaling in.
3 Components
Groups
Logical component. Webserver group or Application group or Database group etc.
Configuration Templates
Groups uses a launch template or a launch configuration as a configuration template for its EC2 instances.
You can specify information such as the AMI ID, instance type, key pair, security groups, and block device mapping for your instances.
Scaling Options
Scaling Options provides several ways for you to scale your Auto Scaling groups.
For example, you can configure a group to scale based on the occurance of specified conditions (dynamic scaling) or on a schedule.
Scaling Options
Maintain current instance levels at all times
- You can configure your Auto Scaling group to maintain a specified number of running instances at all times.
- To maintain the current instance levels, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling performs a periodic health check on running instances within an Auto Scaling group.
- When Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling finds an unhealthy instance, it terminates the instance and launches a new one.
Scale manually
- Manual scaling is the most basic way to scale your resources, where you specify only the change in the maximum, minimum, or desires capacity of your Auto Scaling group.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling manages the process of creating or terminating instances to maintain the updated capaciy.
Scale based on a schedule
- Scaling by schedule means that scaling actions are performed automatically as a function of time and date.
- This is useful when you know exactly when to increase or decrease the number of instances in your group, simply because the need arises on a predictable schedule.
Scale based on demand
- A more advanced way to scale your resources - using scaling policies - lets you define parameters that control the scaling process.
- For example, let's say that you have a web application that currently runs on two instances and you want the CPU utilization of the Auto Scaling group to stay at around 50 percent when the load on the application changes.
- This method is useful for scaling in response to changing conditions, when you don't know when those conditions will change.
- You can set up Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to respond for you.
Use predictive scaling
- You can also use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling in combination with AWS Auto Scaling to scale resources across multiple services.
- AWS Auto Scaling can help you maintain optimal availability and performance by combining predictive scaling and dynamic scaling (proactive and reactive approaches, respectively) to scale your Amazon EC2 capacity faster.
Configure Auto Scaling Group
Navigate to EC2 > AUTO SCALING > Launch Configuration > Create launch configuration
Choose AMI
Choose Instance Type
Configuration details
| Purchasing option | Enable to request Spot Instances |
| IAM role | Select your applicable IAM role |
| Advanced Details | |
| User data | Supply bootstrap scipt to be executed by all your EC2 instances at launch. |
| IP Address Type | |
Add Storage
Configure Security Group
After this setup, no EC2 instances have been launched, you have only created a launch configuration.
You must click on the button 'Create an Auto Scaling group using this launch configuration' to create an Auto Scaling Group that uses this launch configuration.
Configure Auto Scaling group details
| Launch Configuration | Shows the launch configuration used by this Auto Scaling Group |
| Group Size | Indicate the minimum number of instances |
| Network | Select the VPC you want this group to be in |
| Subnet | You can select 1 or more subnets If you select more than 1 subnet, the EC2 instances will randomly and evenly be created in different subnets. |
| Advanced Details | |
| Load Balancing | You can put this Auto Scaling Group behind a ELB |
Configure scaling options
You can select to keep this group as its initial size or use scaling policies to adjust capacity:
| Scale between | Specify your minimum and maximum number of instances. |
| Metric type | Choose your appropriate metric type |
| Target value | Choose a trigger value (goes above) |
| Instances need | The amount of time that your instances need to warm up. During this time, instances that have been launched will not contribute to the Auto Scaling group metrics. |
Configure Notifications
You can add Notifications when scaling happens (sms, email ect)
Configure Tags
Review
Auto Scaling Group Details
When you delete an Auto Scaling Group, the instances linked to it will also be deleted.
EC2 Instance Termination
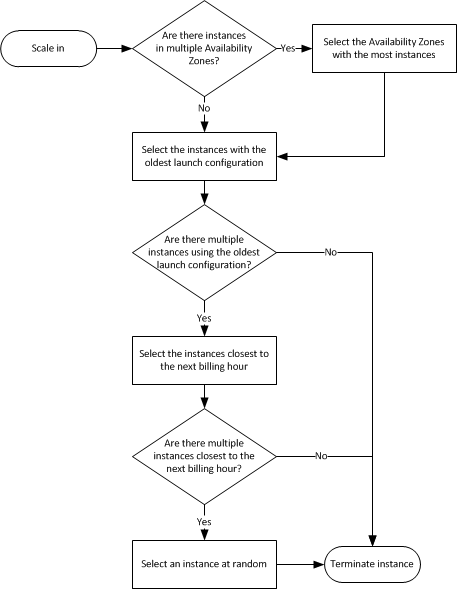
The default termination policy is designed to help ensure that your network architecture spans Availability Zones evenly.
With the default termination policy, the behavior of the Auto Scaling group is as follows:
1. If there are instances in multiple Availability Zones, choose the Availability Zone with the most instances and at least one instance that is not protected from scale in.
If there is more than one Availability Zone with this number of instances, choose the Availability Zone with the instances that use the oldest launch configuration.
2. Determine which unprotected instances in the selected Availability Zone use the oldest launch configuration. If there is one such instance, terminate it.
3. If there are multiple instances to terminate based on the above criteria, determine which unprotected instances are closest to the next billing hour. (This helps you maximize the use of your EC2 instances and manage your Amazon EC2 usage costs.) If there is one such instance, terminate it.
4. If there is more than one unprotected instance closest to the next billing hour, choose one of these instances at random.