Elastic Block Store
What is EBS?
EBS is a virtual hard disk drive and provides persistant block storage volumes for use with EC2 instances in the AWS Cloud.
Each Amazon EBS volume is automatically replicated within its AZ to protect you from component failure, offering high availability and durability.
You can change EBS volume sizes on the fly, including changing the size and storage type.
Volumes will always be in the same AZ as the EC2 instance.
EBS Storage Types
| Volume Type | General Purpose SSD | Provisioned IOPS SSD | Throughput Optimized HDD | Cold HDD | EBS Magnetic |
| Description |
General purpose SSD volume that balances price and performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads. Deliver consistent performance whether an I/O operation is random or sequential. Bootable volume. |
Highest-performance SSD volume designed for mission-critical applications. Deliver consistent performance whether an I/O operation is random or sequential. Bootable volume. |
Low cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput internsive workloads. Deliver optimal performance only when I/O operations are large and sequential. Not a bootable volume. |
Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads Deliver optimal performance only when I/O operations are large and sequential. Not a bootable volume. |
Previous generation HDD. Not a bootable volume. |
| Use Cases | Most workloads | Databases | Big Data & Data Wharehouses | File Servers | Data infrequently accessed |
| API Name | gp2 | io1 | st1 | sc1 | Standard |
| Volume Size | 1 GiB - 16 TiB | 4 GiB - 16 TiB | 500 Gib - 16 TiB | 500 Gib - 16 TiB | 1 GiB - 1 TiB |
| Max. IOPS | 16 000 | 64 000 | 500 | 250 | 40-200 |
| Max. IOPS | 16 000 | 64 000 | 500 | 250 | 40-200 |
Migrating EBS Volumes from one AZ to another
- Select your volume that you want to move to a different region, select Actions > Create Snapshot.
- Snapshots exists on S3. Think of snapshots as a photograph of the disk.
- Snapshots are point in time copies of Volumes.
- Snapshots are also incremental - only the blocks that have changed since your last snapshot are moved to S3.
- To create a snapshot for Amazon EBS volumes that serve as root devices, you should stop the instance before taking the snapshot.
- However you can take a snap while the instance is running.
- You will find Snapshots underneath ELASTIC BLOCK STORE menu item of the EC2 dashboard.
- Select your Snapshot created above, click on Actions > Create Image.
- Note: Virtualization type : Choose 'Hardware-assisted virtualization' to give you to widest variety of instance types.
- You can see images underneath IMAGES > AMIs
- You can select your image and click 'Launch'
- At Step 3 of launching your EC2 instance you can now select a different Subnet (hence different region).
- You can also select your AMI and then select 'Copy AMI' to then launch your AMI into a different region.
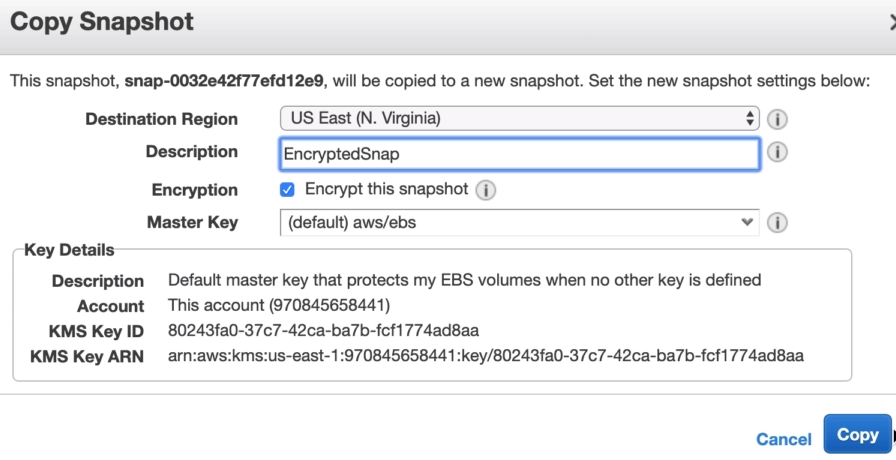
Encrypted Root Device Volumes & Snapshots
- You can now encrypt Root Device volumes when launching an EC2 instance. - When you create a volume unencrypted, you can follow these steps to encrypt it: - Navigate to 'Volumes' under 'ELASTIC BLOCK STORE' and select your volume. - Click on Actions > Create Snapshot. - Select Snapshot under Snapshots. - Click on Actions > Copy. - When you copy the Snapshot, you can select a different Destination Region and also select Encryption.
- Select the new encrypted volume and click on Actions > Create Image. - Click on newly created AMI under IMAGES > AMIs - Click on Launch and follow the steps to launch your EC2 instance.
EBS snapshots occur asynchronously.
This means that the point-in-time snapshot is created immediately, but the status of the snapshot is pending until the snapshot is complete (when all of the modified blocks have been transferred to Amazon S3), which can take several hours for large initial snapshots or subsequent snapshots where many blocks have changed.
While it is completing, an in-progress snapshot is not affected by ongoing reads and writes to the volume hence, you can still use the volume.
EC2 & Performance
If the goal is to increase the write performance of the database hosted in an EC2 instance, you can achieve this by either setting up a standard RAID 0 configuration or simply by increasing the size of the EC2 instance.
Some EC2 instance types can drive more I/O throughput than what you can provision for a single EBS volume.
You can join multiple gp2, io1, st1, or sc1 volumes together in a RAID 0 configuration to use the available bandwidth for these instances.
With Amazon EBS, you can use any of the standard RAID configurations that you can use with a traditional bare metal server, as long as that particular RAID configuration is supported by the operating system for your instance.
This is because all RAID is accomplished at the software level.
For greater I/O performance than you can achieve with a single volume, RAID 0 can stripe multiple volumes together; for on-instance redundancy, RAID 1 can mirror two volumes together.
Take note that HVM AMIs are required to take advantage of enhanced networking and GPU processing.
In order to pass through instructions to specialized network and GPU devices, the OS needs to be able to have access to the native hardware platform which the HVM virtualization provides.
Examp Tips
- When you terminate an EC2 instance the root device volume will also be deleted. - Any additional device volumes will persist if you haven't explicitly selected the 'Terminate on deletion' option for these volumes. - To move an EC2 volume from one AZ to another: - 1 Take a Snapshot of it. - 2 Create an AMI from the Snapshot. - 3 Use AMI to launch the EC2 instance in a new AZ. - To move an EC2 volume from one region to another: - 1 Take a Snapshot of it. - 2 Create an AMI from the Snapshot. - 3 Copy the AMI from one region to the other. - 4 Then use the copied AMI to launch the new EC2 instance in the new region. - To encrypt an unencrypted root device volume: - 1 Take a Snapshot of the unencrypted root device volume. - 1 Create a copy of the Snapshot and select the encrypt option. - 2 Create an AMI from the Snapshot. - 4 Use AMI to launch new encrypted instances. - AWS does not copy launch permissions, user-defined tags, or Amazon S3 bucket permissions from the source AMI to the new AMI. - If an Amazon EBS volume is an additional partition (not the root volume), can I detach it without stopping the instance? Yes, but it might take some time. - You can add multiple volumes to an EC2 instance and then create your own RAID 5/RAID 10/RAID 0 configurations using those volumes. Yes - Can I delete a snapshot of an EBS Volume that is used as the root device of a registered AMI? No - Which AWS CLI command should I use to create a snapshot of an EBS volume? aws ec2 create-snapshot - Can you attach an EBS volume to more than one EC2 instance at the same time? Yes, as of Feb 2020 you can attach certain types of EBS volumes to multiple EC2 instances. https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-multi-attach-for-provisioned-iops-io1-amazon-ebs-volumes/