Entity Framework
NuGet Packages
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore | |
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer | |
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools |
Create your Models
Create a new folder called 'Model'.
Model classes will represent any table that you want to create in your database.
Set Connection String
Open appsettings.json file and add your connection string:
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=YourServerName;Database=YourDatabaseName;User Id=YourUserName;Password=YourPassword"
}
Add DbContext class
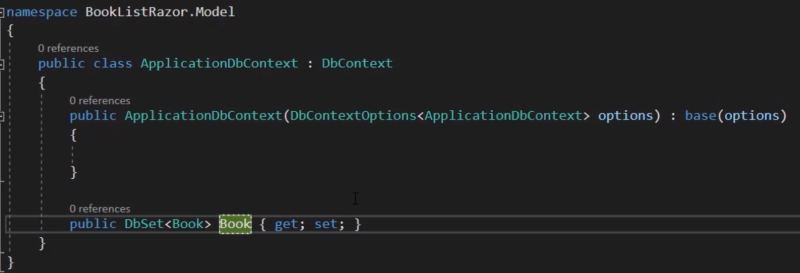
Add a new class inside the Models folder called 'ApplicationDbContext.cs'
Configure Startup.cs class file
ConfigureServices()
services.AddDbContext
Push your model to the database
Navigate to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console
add-migration AddBookToDB
This will create a script that will add the applicable tables to the database when executed.
update-database
This will execute the migration script created above.
Add new Model
When you create a new model, you have to make a change to the ApplicationDBContext.cs class
public DBSet
This will create a new DBContext model to your Entity Framework using the model Category that you created in your model folder.
Navigate to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console
add-migration AddCategoryToDB
This will create a script that will add the applicable tables to the database when executed.
update-database
This will execute the migration script created above.
Read data from Database
Using dependency injection that we implemented in StartUp.cs, we can utilize the ApplicationDBContext to read data from the database.
In your controller you define the ApplicationDBContext.
private readonly ApplicationDBContext _db;
public CategoryController(ApplicationDBContext db)
{
_db = db;
}
public async Task Index()
{
return View(await _db.Category.ToListAsync());
}
This will create a new DBContext model to your Entity Framework using the model Category that you created in your model folder.
Navigate to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console
add-migration AddCategoryToDB
This will create a script that will add the applicable tables to the database when executed.
update-database
This will execute the migration script created above.
Post Action
Whenever you do a Post action you have to add the [HttpPost] to let MVC know it is a http post method.
Also include the [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] to protect the post against SQL Injection and Cross-Site attacks
//POST - CREATE
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task Create(Category category)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
_db.Category.Add(category);
await _db.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index)); //redirect to an action and use nameof to avoid spelling mistakes
}
return View(category);
}
Update Action (GET & POST)
Whenever you do a Post action you have to add the [HttpPost] to let MVC know it is a http post method.
Also include the [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] to protect the post against SQL Injection and Cross-Site attacks
//GET - EDIT
public async Task Edit(int? id)
{
var category = await _db.Category.FindAsync(id);
return View(category);
}
//POST - EDIT
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task Edit(Category category)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
_db.Category.Update(category);
await _db.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index)); //redirect to an action and use nameof to avoid spelling mistakes
}
return View(category);
}
Delete Action
//GET - DELETE
public async Task Delete(int? id)
{
var category = await _db.Category.FindAsync(id);
return View(category);
}
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")] //when you have duplicate signatured for GET and POST
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task DeleteAction(int id)
{
var category = await _db.Category.FindAsync(id);
if (category == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_db.Category.Remove(category);
await _db.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index)); //redirect to an action and use nameof to avoid spelling mistakes
}
Create model (SubCategory.cs) with foreign key reference
... other properties
[Required]
[Display(Name = "Category")]
public int CategoryId { get; set; }
[ForeignKey("CategoryId")]
public virtual Category Category {get; set;}
Remember to also add the SubCategory in the ApplicationDBContext.cs
public DBSet SubCategory {get; set;}
add-migration AddSubCategoryToDB
This will create a script that will add the applicable tables to the database when executed.
update-database
When creating the GET for SubCategory, you want to include the name of Category as well, thus the following change is needed:
var subCategories = await _db.SubCategory.Include(s=>s.Category).ToListAsync();
return View(subCategories);
